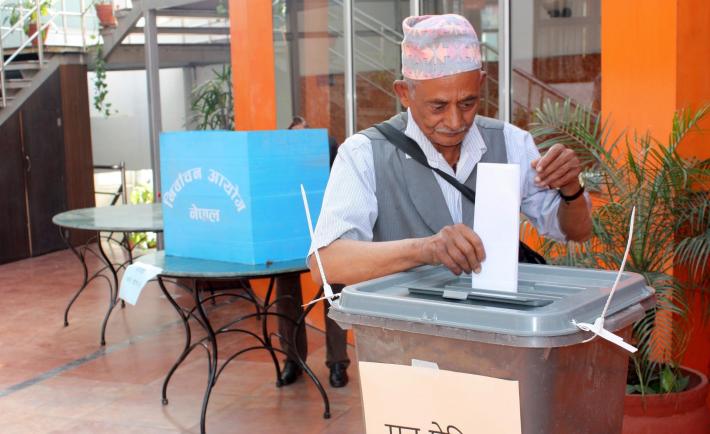
A political party participant casts his vote during a mock election exercise on April 25, 2017 in Nepal. Through mock elections, candidates familiarized themselves with the voting process in order to conduct more effective voter outreach.
Since the end of its brutal decade-long civil war in 2006, Nepal has undergone a rocky, but peaceful democratic transition. The country has transitioned through the dissolution of its monarchy, the restoration of parliament, a devastating earthquake, the adoption of a new constitution, and the establishment of a federal republic. However, persistent poverty, the geographic isolation of many villages, and the marginalization of certain ethnic communities pose severe challenges to the nation’s economic and political development. Since the adoption of a new constitution in September 2015, significant progress has been made to improve government effectiveness, increase social inclusion and cohesion, and increase the responsiveness of the country’s representative institutions such as parliament and its political parties. Through on-the-ground engagement at each step in this time of change, NDI has worked to ensure that Nepali democracy reflects what matters to citizens, most recently in the country’s watershed local elections.